Connecting two monitors together can open up a whole new world of possibilities for your workspace or entertainment setup. Whether you’re seeking increased productivity, enhanced gaming experiences, or just want a larger screen for multitasking, knowing how to connect a monitor to another monitor is a crucial skill for any computer user.
Why Connect Two Monitors?
Before jumping into the setup process, it’s important to understand the benefits of having two monitors. A dual-monitor configuration brings a host of advantages for both productivity and enjoyment:
- Smarter Multitasking: A second monitor means a more effective work style in which you spread out. You can have email up on one screen and be working on a project on the other, or your calendar and to-do list up while you write reports.
- Immersive Gaming: For gamers, the addition of a second monitor provides a more dynamic experience. One can have a game on, while another could be dedicated to chat, streaming, or watching performance statistics.
- Smarter Entertainment: With more screen real estate, it will be so much easier to watch movies, edit videos, or work on graphic design projects. You won’t have to keep minimizing one program just to access another.
Now that we have discussed why you would want to connect a monitor to another, let’s see how to do it.
How to Connect a Monitor to Another Monitor
Setting up multiple monitors typically relies on a few key components: cables, ports, and maybe a graphics card upgrade. Here’s how you can connect your monitors correctly.
1. Check Available Ports on Your CPU and Monitor
The very first thing you should do before connecting two monitors is to ensure that your computer supports multiple displays. Here’s how you can verify:
- The Ports on Your Computer: Most modern PCs and laptops support connecting multiple monitors. Your computer will be equipped with various ports: HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, or USB-C are the most common; they are used for video output to connect monitors.
- Ports on Your Monitor: Similarly, your monitor will have at least one input port, usually HDMI or DisplayPort, and sometimes VGA. Check the input ports on your monitor before purchasing cables or adapters.
2. Choose the Right Cable(s)
Once you’ve confirmed that both your monitor and CPU have compatible ports, you’ll need to find the right cable to establish the connection. Here’s a breakdown of popular cable types:
- HDMI – High Definition Multimedia Interface: HDMI cables are one of the most common and versatile types of cables. They support high-definition video and audio. For most users, the use of HDMI is usually simple and effective.
- DisplayPort: With a high usage rate in high-ended displays and graphics, its resolutions and refresh rates stand a notch above those attainable with HDMI. That would be ideal for both gaming and graphic design workstation setups. If your monitor and graphics card support the connection, this may very well be your best choice.
- VGA: This is an older standard, though less common today, still finds a place in some of the legacy monitors and PCs. It has mainly been used for monitors at a standard resolution.
- USB-C: Some newer monitors—mostly those made for macOS—may have USB-C for connections. This keeps the area around your monitor clean and simple without other adapters.
First, ensure you have the right cables to match your monitor and computer’s ports. If they are different, there are easy, cheap adapters like HDMI-to-DisplayPort adapters you can buy.

3. Connect the Monitors to Your Computer
Once you have prepared the cables, it is now time to connect the monitors. Here is the general process:
- First Monitor Connection: Connect one end of the cable to your computer’s video output port and connect the other end to the input port of the monitor.
- Second Monitor Connection: Plug the proper cable into another available video output port on your computer for the second monitor, and then connect the other end to the second monitor.
If this is the case, your graphics card may need more than one video output port in order to handle the two-monitor setup. You will need to upgrade the graphic card or split the output using an adapter over to both monitors if the computer has only one output port.
4. Setting the Display Settings
After connecting all monitors physically, the following action should be taken over your computer to change the display settings. Here’s how it works with popular operating systems:
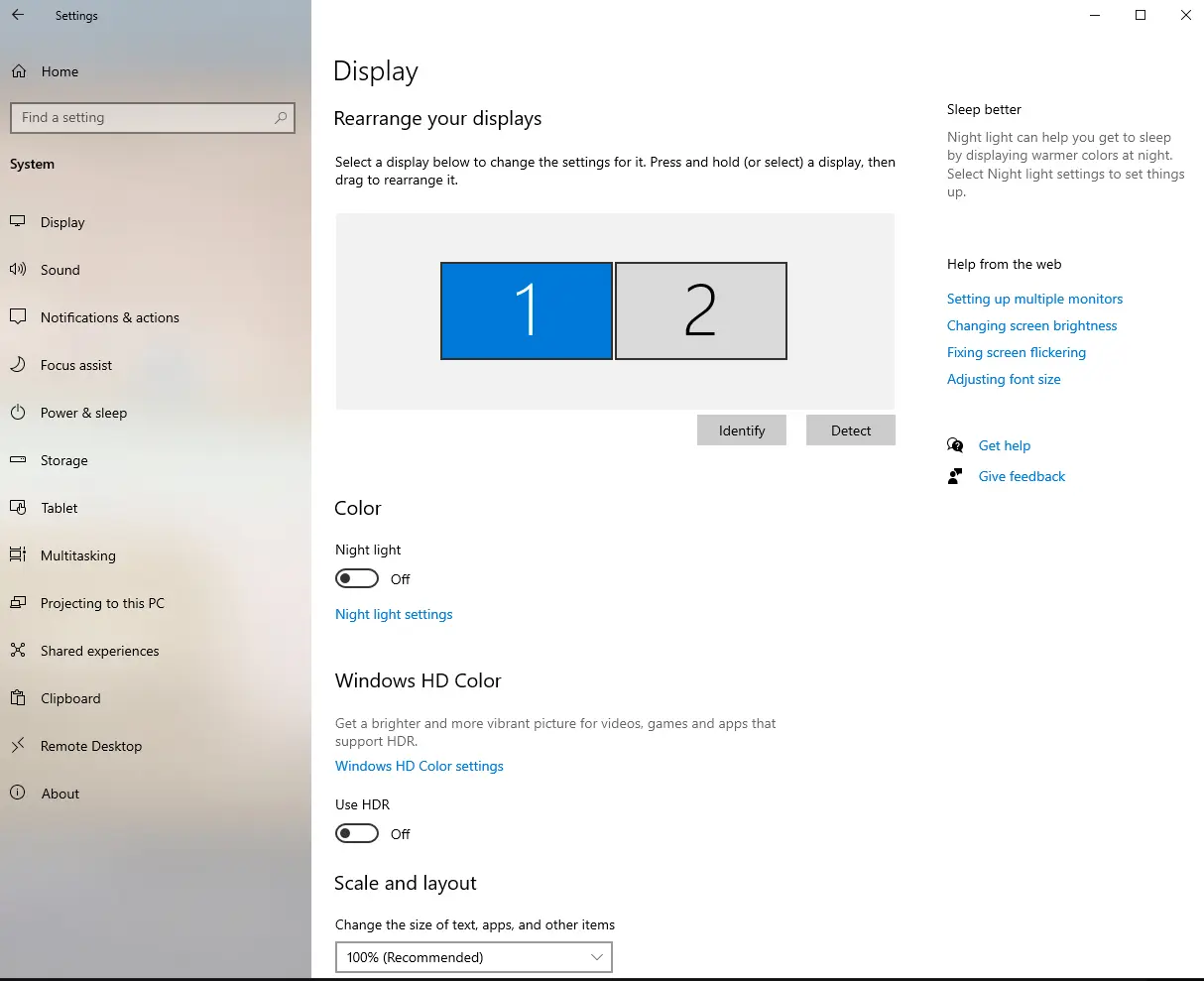
In Windows:
- Right-click your desktop and choose Display Settings.
- Scroll down, click on Multiple displays.
- You now have options to Extend or Duplicate your displays. The option to Extend creates a wider screen across both monitors, whereas the Duplicate option will display the same content on both monitors. Select whichever fits best and click Apply.
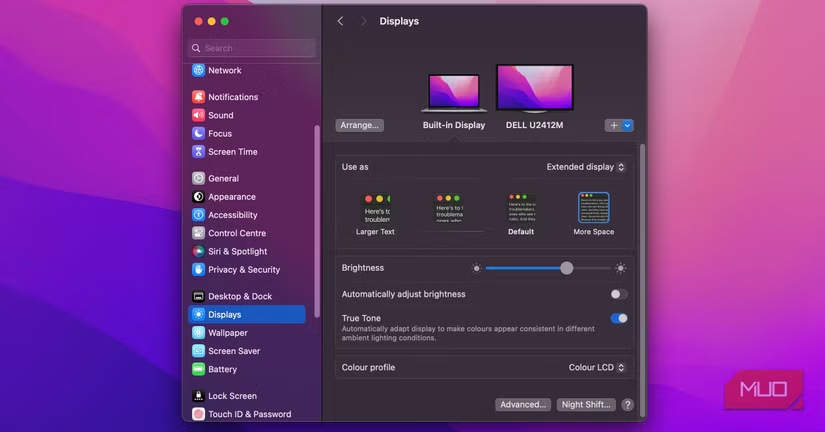
In macOS:
- Go to System Preferences > Displays.
- Click the Arrangement tab. You can drag and set the displays as if you place them in reality on the desk.
5. Adjust Resolution and Orientation
Depending on how you setup your monitors, you can adjust Resolution and Orientation in order for an optimal display:
- Resolution: First, make sure that the resolutions of the two monitors are at their best resolution to avoid having stretched images or blurry texts on the screen. Under Windows, this is edited in Display Settings; in macOS, it is under the Displays preferences.
- Orientation: You might want to change the orientation if any of your monitors are on a vertical position. The Display Settings in both operating systems allow you to edit this.
How to Optimize a Dual-Monitor Setup
Once you get your monitors up and running, you may want to optimize your setup:
- Put your monitors at the right height: For ideal ergonomics, position the monitors so that the top of the screen is at or slightly below eye level, which would provide an optimum viewing angle.
- Adjust brightness and color settings: Ensure that both monitors have similar brightness and color settings to avoid distraction caused by inconsistent display properties.
- Keep your workspace tidy: Use cable organizers to prevent wires from cluttering your desk, and ensure that both monitors are placed at comfortable viewing angles.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Although connecting two monitors is usually easy, you may encounter a few problems. Here are some of the issues and how to fix them:
- Monitor Not Detected: First of all, check your connection, make sure that cables are properly inserted, and restart your computer. If it still doesn’t detect the monitor, then check whether the monitor is turned on and select the correct input source.
- Resolution Issues: If the screen is blurry or pixelated, enter the Display Settings and make sure that the native resolution of both monitors is selected.
