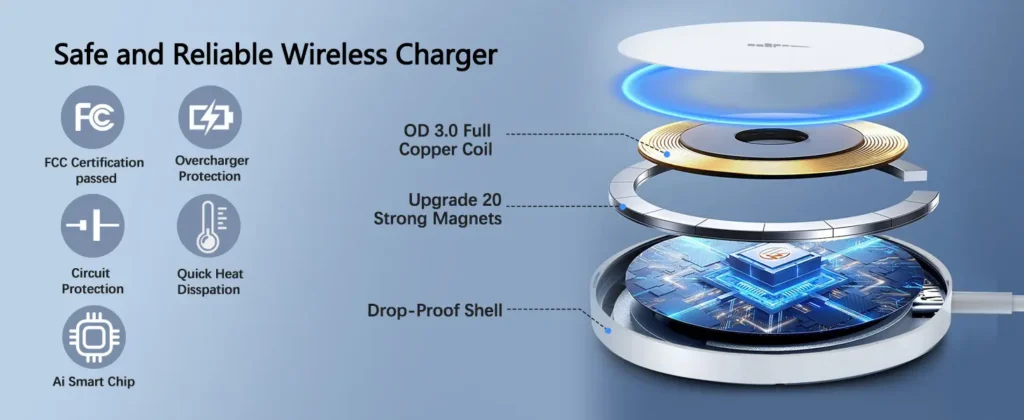
Wireless charging technology has grown over the years to revolutionize the way we power our devices. No tangled cords and plugs are required to charge, thus making it easier and more convenient. But have you ever wondered how wireless charging works and what makes it tick? Among the different types of wireless charging, two in particular stand out: inductive and resonant charging. While both fulfill the same basic purpose—powering your devices wirelessly—they do it differently, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This article will take a closer look into these two technologies, comparing their functionalities, uses, and which one might go well with your needs.
Wireless Charging: The Basics
Before going into the types of wireless charging, let me first make it clear what it is. The principle of electromagnetic induction is applied in wireless charging. Instead of having a physical connection, that is a cable, there is an electromagnetic field through which power is transferred by coils on both the charger and the device. While that sounded like magic, the science is efficient and workable.
In the broad category of wireless charging, there have evolved two major methods: inductive and resonant charging. Let’s take a glimpse at how each of these works.
Inductive Charging: How Does It Work?
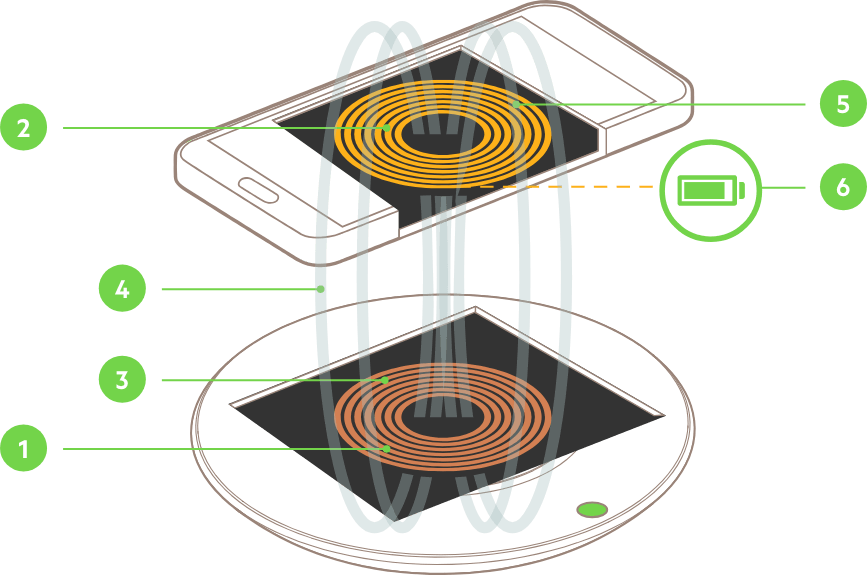
Inductive charging is the most common form of wireless charging and arguably the first that comes to most people’s minds when the subject is brought up. It works through two magnetic coils: one in the charger and one in your device. Here’s how it works: The charger generates a magnetic field through its coil.
Your device also contains a coil; the energy is absorbed from the magnetic field by your device and converted back into electrical energy to charge the battery.
This method is highly efficient for powering devices at relatively short distances. The coil in both the charger and device must be precisely aligned to ensure efficient power transfer. That’s why you’ll often hear of a charging pad for your phone or an Apple Watch charger—these devices are designed specifically for induction.
Pros of Inductive Charging
- Ease: It is pretty simple to operate inductive charging for such devices as smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds—just put it on the charger and let them fill up!
- Safety: The physical contact in Inductive Charging is almost zero, so wear and tear are greatly reduced. Plus, the charging pad tends to stay cool during operation, making it a safe option.
- Widely Used: It’s the standard technology in the majority of wireless chargers on the market today. From your desk to your car, chances are you’ve already used an inductive wireless charger.
Cons of Inductive Charging
- Limited Distance: The efficiency drops when the distance between the charger and device increases, which means they need to be in close proximity for best results.
- Alignment Sensitivity: For efficient charging, the coils should be aligned; any partial misalignment may result in weak or no charge at all.
- Heat Generation: Energy transmission generates heat, and the inefficiency that sometimes occurs during inductive charging has been known, at times, to generate more heat than that from wired charging.
Resonant Charging: The Next Step in Wireless Power
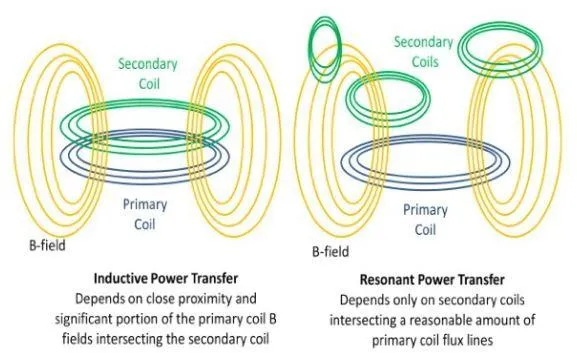
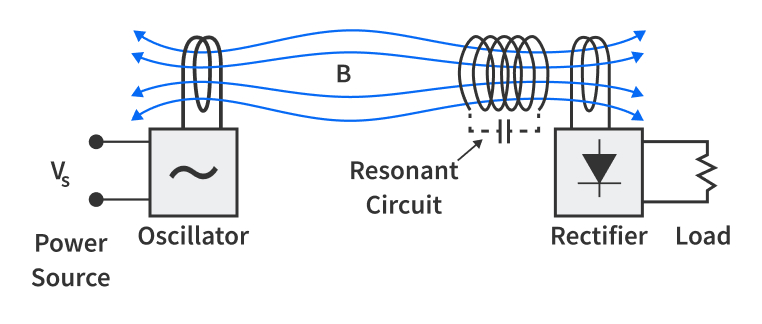
While inductive charging is both reliable and efficient, resonant charging really takes the limit off of wireless charging. Resonant charging is similar to inductive charging but for a couple of key reasons, it is very different. In this method, both the charger and device are tuned into the same resonant frequency, allowing energy to transfer over larger distances.
Here’s how resonant charging works:
This magnetic field is stronger and can extend over a little greater distance compared to inductive charging.
Since devices and chargers can be tuned to specific frequencies, efficient power transfer at a distance is enabled and thus allows for charging when alignment is less critical.
In practice, resonant charging can power multiple devices at once or charge devices placed further from the source. Think of it like turning a radio dial to just the right frequency: once the device is at the right frequency, the energy flow becomes stronger.
Pros of Resonant Charging
- Larger Range: The resonance-based recharging doesn’t need exact positioning, and it could work at distances as large as a few centimeters between the device and the charger.
- Multi-device Charging: Unlike induction-based charging, resonant chargers can transfer power to more than one device at once. This makes it perfect for charging stations or environments such as offices or homes.
- Less Heat Generation: Since the system is optimized for efficiency at higher distances, resonant charging tends to generate less heat than the inductive method.
Disadvantages of Resonant Charging
- Cost and Complexity: The technology for resonant charging tends to be more expensive and slightly more complex compared to the inductive systems.
- Limited Availability: Up until now, resonant chargers are not as available or as widely adopted as inductive chargers, though they do find growing acceptance in niche markets like furniture charging systems or automotive applications.
- Still Evolving: While resonant charging sounds very impressive, this is still a technology in development. Incompatibility between different device types and charger types can make it difficult to expand on a large scale.
Inductive vs. Resonant Charging: Key Differences
Let’s quickly do a comparison of the two:
| Feature | Inductive Charging | Resonant Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Shorter—require close contact | Longer range—works over a few centimeters |
| Device Alignment | Sensitive, precise alignment necessary | More forgiving, less precise alignment |
| Power Transfer | Effective at smaller, personal devices | Can charge multiple devices at once |
| Cost | Lower cost, common in most products | Higher cost, often used in high-end tech |
| Heat Generation | Potential to get hot, depending on efficiency | Tends to generate less heat |
| Popularity | Very popular and widely available | Emerging, not yet mainstream |
Which One Is Better for You?
Inductive and resonant have their relative merits, respectively, but each is better than the other for different needs. If you’re after an inexpensive, uncomplicated way of keeping your smartphone juiced up, inductive is probably your best bet. It’s integrated into virtually all phones, tablets, and many other gadgets today. Plus, its compatibility with Qi standard allows you to charge most devices with wide-range chargers.
If, however, you consider multi-device charging or have requirements where the device could be further away from the charging surface, then resonant charging might be in your near future. Continuous technological advancement is seeing appliances and furniture in general being integrated with resonant wireless chargers to ensure one is comfortable within different areas without going through stressful times.
Explore ONext Wireless Products
Magnetic Wireless Chargers Station, 3 in 1 Wireless Charger Fast Max Charging for iPhone 16 15 14 13 12 Pro Max Plus, Wireless Charging Stand for Apple Watch Series & Air pods 3 2 Pro, Gifts for Men
Quick Wireless Charger 20W Max Wireless Charging Pad Compatible with iPhone ,ipad ,AirPods, Wireless Charge Mat for Multidevice